前言
对于函数绑定(Function binding)很有可能是大家在使用JavaScript时最少关注的一点,但是当你意识到你需要一个解决方案来解决如何在另一个函数中保持this上下文的时候,你真正需要的其实就是 Function.prototype.bind() ,只是你有可能仍然没有意识到这点。
第一次遇到这个问题的时候,你可能倾向于将this设置到一个变量上,这样你可以在改变了上下文之后继续引用到它。
一. bind的语法
bind() 方法的主要作用就是将函数绑定至某个对象,bind() 方法会创建一个函数,函数体内this对象的值会被绑定到传入bind() 函数的值。
1.1 定义
bind()的定义如下:
The bind() method creates a new function that, when called, has its this keyword set to the provided value, with a given sequence of arguments preceding any provided when the new function is called.
bind() 函数会创建一个新函数(称为绑定函数),新函数与被调函数(绑定函数的目标函数)具有相同的函数体。当目标函数被调用时 this 值绑定到 bind() 的第一个参数,该参数不能被重写。
1.2 原理
可以用如下代码模拟bind()的原理:
?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Function.prototype.bind = function(context) {
var self = this; // 保存原函数
return function() { // 返回一个新函数
return self.apply(context, arguments); // 执行新函数时,将传入的上下文context作为新函数的this
}
}
|
1.3 语法
?
| 1 |
Function.prototype.bind(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])
|
二. bind的应用场景
2.1 实现对象继承
?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
var A = function(name) {
this.name = name;
}
var B = function() {
A.bind(this, arguments);
}
B.prototype.getName = function() {
return this.name;
}
var b = new B("hello");
console.log(b.getName()); // "hello"
|
2.2 事件处理
?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
var paint = {
color: "red",
count: 0,
updateCount: function() {
this.count++;
console.log(this.count);
}
};
// 事件处理函数绑定的错误方法:
document.querySelector('button')
.addEventListener('click', paint.updateCount); // paint.updateCount函数的this指向变成了该DOM对象
// 事件处理函数绑定的正确方法:
document.querySelector('button')
.addEventListener('click', paint.updateCount.bind(paint)); // paint.updateCount函数的this指向变成了paint
|
2.3 时间间隔函数
?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
var notify = {
text: "Hello World!",
beforeRender: function() {
alert(this.text);
},
render: function() {
// 错误方法:
setTimeout(this.beforeRender, 0); // undefined
// 正确方法:
setTimeout(this.beforeRender.bind(this), 0); // "Hello World!"
}
};
notify.render();
|
2.4 借用Array的原生方法
?
| 1 2 3 4 |
var a = {};
Array.prototype.push.bind(a, "hello", "world")();
console.log(a); // "hello", "world"
|
三. bind()方法的浏览器兼容性
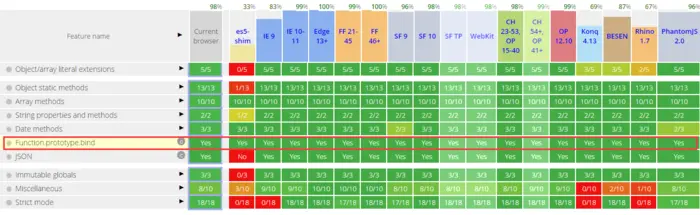
四. bind()的兼容性写法
?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
if (!Function.prototype.bind) {
Function.prototype.bind = function() {
var self = this, // 保存原函数
context = [].shift.call(arguments), // 需要绑定的this上下文
args = [].slice.call(arguments); // 剩余的参数转成数组
return function() { // 返回一个新函数
// 执行新函数时,将传入的上下文context作为新函数的this
// 并且组合两次分别传入的参数,作为新函数的参数
return self.apply(context, [].concat.call(args, [].slice.call(arguments)));
}
};
}
|
五. bind与 call/apply方法的区别
共同点:
都可以改变函数执行的上下文环境;
不同点:
bind: 不立即执行函数,一般用在异步调用和事件; call/apply: 立即执行函数。
